Neuro Plus Brain and Focus
Neuro Plus Brain and Focus
This supplement helps by improving mental clarity and focus, boosting intelligence levels, memory function, and increasing your level of concentration and alertness. As an added bonus, Neuro Plus can provide you with an increased level of energy and improved mood.*
This supplement helps by improving mental clarity and focus, boosting intelligence levels, memory function, and increasing your level of concentration and alertness. As an added bonus, Neuro Plus can provide you with an increased level of energy and improved mood.
Neuro Plus Brain and Focus is formulated to boost cognitive function, mental clarity, focus, immune function, and energy production.Our product is synthesized utilizing the latest scientific research and formulated with high-quality ingredients.
Our formula is third-party independently tested for heavy metals, impurities, made in the USA, GMP certified, and produced in an FDA registered facility. 1% of the supplements on the market can match our world-class standards.
Serving Size: 2 Capsules;
Capsules Per Container: 60;
Bottle Color: White;
Bottle Size: 175cc;
Lid Color: White
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
Couldn't load pickup availability






- Neuro Plus Brain and Focus is formulated to boost cognitive function, mental clarity, focus, immune function, and energy production.
- Our product is synthesized utilizing the latest scientific research and formulated with high-quality ingredients.
- Our formula is third-party independently tested for heavy metals, impurities, made in the USA, GMP certified, and produced in an FDA registered facility. 1% of the supplements on the market can match our world-class standards.
Serving Size: 2 Capsules;
Capsules Per Container: 60;
Bottle Color: White;
Bottle Size: 175cc;
Lid Color: White
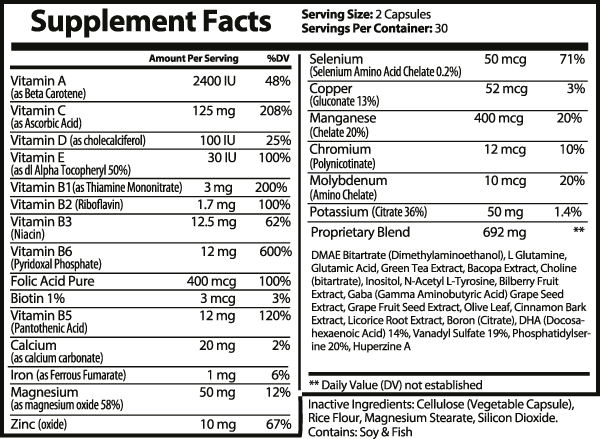
Vitamin A
- Supports vision health, skin health, immune health, and increases antioxidant support (182, 183).
- Reduces inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species, increasing l-glutathione production (182, 183).
- Improves visual health via increased plasma vitamin A in macular tissues (182, 183).
Vitamin C
- Enhances immune, cardiovascular, skin, cognitive, fat-burning, and digestive health (97, 98).
- Boosts immune health by increasing oxidant scavenging and aiding immune cell activity (97, 98).
- Increases carnitine biosynthesis, supporting fat burning (97, 98).
- Accelerates bone healing and collagen synthesis while reducing oxidative stress (98).
Vitamin D
- Supports exercise performance, immune health, muscle growth, bone health, hormonal balance, and cardiovascular health (77-79).
- Enhances sexual health, strength, and positive mood (77-79).
- Improves cardiovascular and immune functions by reducing inflammation and muscle damage (77-79).
Vitamin E
- Promotes immune function, cognitive health, cardiovascular health, and bone health (204-208).
- Neutralizes free radicals, improves T lymphocyte-mediated immune response, and lowers cholesterol (204-208).
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Supports aerobic energy metabolism, cell growth, and cardiovascular health (94).
- Acts as a neuroprotective agent and improves heart function (94, 95).
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Aids in converting and activating other B vitamins, producing red blood cells, and energy production (92, 93).
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Supports cardiovascular health by inhibiting liver triglyceride synthesis and increasing HDL levels (9).
- Reduces the conversion of VLDL into LDL and regulates gene expression and cell death (9).
- Protects against diseases like Pellagra and Crohn's while improving tumor sensitivity to radiation (9-12).
Vitamin B6
- Cofactor in 150+ enzymatic reactions involved in blood sugar regulation, immunity, and neuronal health (38, 40).
- Lowers blood sugar levels and serves as an antioxidant (38, 39).
Folic Acid
- Supports proper cell growth and DNA synthesis (65).
Biotin
- Enhances energy conversion, hair, skin, and cognitive function (213, 214).
Vitamin B5
- Supports energy production, cell repair, cognitive function, and memory (96).
Calcium
- Promotes bone health, muscle function, and cardiovascular health (36, 37).
- Regulates bone mineralization and prevents preeclampsia (36, 37).
Iron
- Aids red blood cell formation, immune function, and oxygen uptake in iron-deficient individuals (215-217).
Magnesium
- Supports nerve function, muscle contractions, cardiovascular health, and reduces anxiety (90, 91).
- Regulates blood pressure and glucose levels (90, 91).
Zinc
- Boosts immune function, skin health, and cognitive performance (172, 173).
- Enhances immune cell activation and neuronal signaling (172, 173).
Selenium
- Antioxidant supporting cardiovascular, cognitive, thyroid, and immune health (145-147).
Copper
- Regulates blood sugar, energy metabolism, and cholesterol management (143, 144).
Manganese
- Involved in enzymatic antioxidant reactions, bone health, and blood sugar regulation (148, 149).
Chromium
- Supports insulin function and blood sugar regulation (218, 219).
Molybdenum
- Increases enzymatic reactions for detoxification (150).
DMAE Bitartrate
- Enhances acetylcholine levels in the brain, supporting cognitive function.
L-Glutamine
- Improves immune function, exercise recovery, and gut health (18).
Glutamic Acid
- Enhances cognitive focus (220).
Green Tea Extract
- Antioxidant supporting blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, and fat burning (25, 26).
Choline
- Vital for cell membrane integrity, fat metabolism, and nervous system function (62-64).
Inositol
- Supports liver detoxification, metabolic syndrome, and antioxidant activity (221, 222).
N-Acetyl Tyrosine
- Enhances memory, cognitive flexibility, and dopamine synthesis (60, 61).
Bilberry Fruit
- Promotes vision health and cardiovascular function (223, 224).
Grape Seed Extract
- Reduces blood pressure and DNA damage while improving collagen and bone strength (31).
Olive Leaf
- Supports cardiovascular health, antioxidant function, and blood sugar regulation (224-226).
Licorice Root
- Offers anti-inflammatory, anti-allergenic, and antimicrobial properties (177).
Boron
- Supports bone health, muscle function, hormonal balance, and immunity (180).
DHA (Fish Oil)
- Enhances cardiovascular, immune, cognitive, and digestive health, while aiding exercise recovery (73-76).
Vanadyl Sulfate
- Regulates blood sugar through improved insulin sensitivity (227).
Phosphatidylserine
- Boosts cognitive function, memory, focus, and stress reduction (228, 229).
Huperzine A
- Supports memory and combats neurodegenerative diseases (230).
Suggested Use: As a dietary supplement take two (2) veggie capsules once a day. For best results take 20-30 minutes before a meal with an 8 oz glass of water, or as directed by your health care professional.
Our Formula Vs other formulas on the market.
Our Formula
- Uses third-party independently tested ingredients that are made in the USA, GMP certified, and made in an FDA registered facility.
- Uses high-quality nutraceuticals in an effective evidence-based and efficaciously dosed formula.
Other Formula
- Source cheap ingredients from heavily polluted soils. Even “organic” supplements not third-party tested have been removed by FDA due to high levels of heavy metals.
- Uses cheap sources of nutraceuticals that contain high amounts of fillers, heavy metals, and is formulated without evidence-based dosages.
No FAQs available.







